Description
Given a non-empty binary tree, find the maximum path sum.
For this problem, a path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along the parent-child connections. The path must contain at least one node and does not need to go through the root.
Example 1:
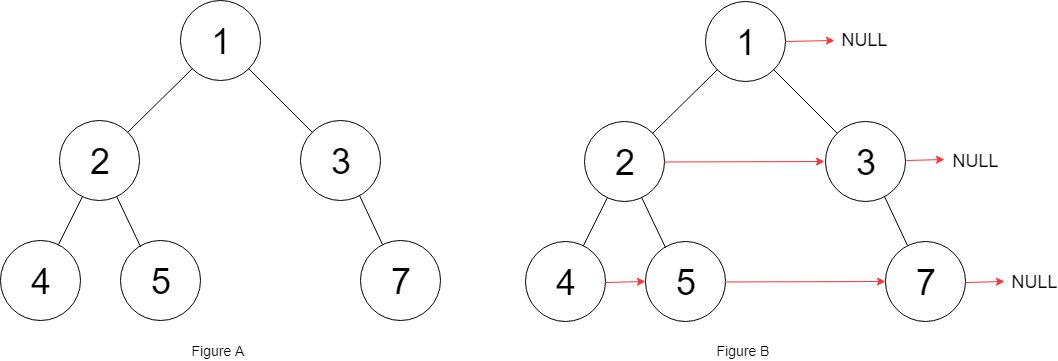
1 | Input: [1,2,3] |
Example 2:
1 | Input: [-10,9,20,null,null,15,7] |